
06 Mar SaaS vs. Traditional Software: Which One is Right for Your Business?
Businesses rely on software solutions to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and improve customer experiences. With technology evolving, companies must decide between Software as a Service (SaaS) and traditional software. Each option has advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to understand their differences before making a decision.
This article explores the key differences, benefits, and drawbacks of SaaS and traditional software to help you determine which solution best fits your business needs.
1. What is SaaS?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based software delivery model where applications are hosted on external servers and accessed via the internet. Instead of installing the software on local machines, users log in through a web browser.
Examples of SaaS Applications:
- Google Workspace (Docs, Sheets, Gmail) – Cloud-based productivity tools
- Salesforce – Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software
- Zoom – Video conferencing platform
- Dropbox – Cloud storage service
SaaS eliminates the need for manual software installation, maintenance, and updates, as everything is managed by the service provider.
2. What is Traditional Software?
Traditional software, also known as on-premise software, requires installation on local computers or company-owned servers. Businesses purchase licenses for the software and are responsible for maintenance, security, and updates.
Examples of Traditional Software:
- Microsoft Office (Standalone version) – Installed directly on a computer
- Adobe Photoshop (Perpetual license) – Requires local installation
- ERP systems hosted on company servers – Used in large enterprises
Traditional software offers more control and customization but requires higher upfront investment and IT management.
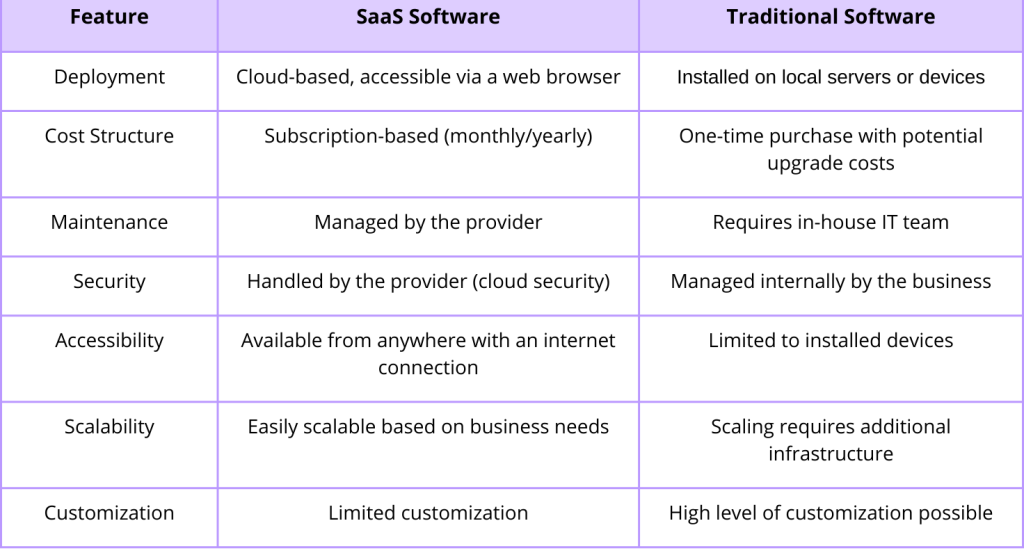
3. Key Differences Between SaaS and Traditional Software
4. Benefits of SaaS Software
A. Lower Upfront Costs
SaaS operates on a subscription model, eliminating the need for large initial investments. Businesses only pay for what they use, making it an affordable option for startups and small businesses.
B. Easy Accessibility
With SaaS, employees can access applications from any device with an internet connection. This flexibility is beneficial for remote teams and businesses with multiple locations.
C. Automatic Updates and Maintenance
The software provider handles updates, bug fixes, and security patches, reducing the workload for in-house IT teams.
D. Faster Deployment
SaaS applications are ready to use without complex installations, allowing businesses to start operations quickly.
E. Scalability
Businesses can easily upgrade or downgrade their subscription plans based on demand, making SaaS ideal for growing companies.
5. Drawbacks of SaaS Software
A. Dependence on Internet Connection
Since SaaS applications are cloud-based, downtime or slow internet can impact accessibility and productivity.
B. Limited Customization
Most SaaS providers offer predefined features that may not fully meet unique business needs. Some companies may require custom-built solutions.
C. Data Security Concerns
Businesses must trust third-party providers with sensitive data. While SaaS companies implement robust security measures, data breaches are still possible.
6. Benefits of Traditional Software
A. Full Control and Customization
Businesses own the software and can modify it to meet specific operational needs, making it ideal for companies with complex workflows.
B. Works Without Internet
Unlike SaaS, traditional software operates offline, ensuring continued functionality even without an internet connection.
C. Greater Data Security
With on-premise storage, businesses control their own security measures, reducing exposure to external cyber threats.
7. Drawbacks of Traditional Software
A. High Initial Costs
Businesses must pay large upfront fees for licenses, hardware, and infrastructure, making it costly for startups.
B. Complex Maintenance and Updates
IT teams must handle security patches, software upgrades, and troubleshooting, requiring dedicated resources.
C. Limited Remote Access
Traditional software is restricted to on-premise devices, making remote work more challenging.
8. When to Choose SaaS Software
SaaS is ideal for businesses that:
- Need cost-effective software with low upfront investment
- Require scalability to adjust as business grows
- Have remote teams that need cloud accessibility
- Want automatic updates and minimal IT maintenance
9. When to Choose Traditional Software
Traditional software is better suited for:
- Businesses that require full control and customization
- Organizations handling highly sensitive data and prefer on-premise security
- Companies that do not rely on internet connectivity for software operations
10. Hybrid Approach: Best of Both Worlds
Some businesses adopt a hybrid approach, combining SaaS and traditional software to balance flexibility and control.
Examples of Hybrid Approaches:
- Hosting an ERP system on-premise while using SaaS-based CRM
- Running security-sensitive applications locally while utilizing cloud-based collaboration tools
This approach allows businesses to leverage cloud benefits while retaining on-premise control over critical data.
11. How PT. KDN Can Help
Choosing between SaaS and traditional software depends on business needs, budget, and long-term goals. At PT. KDN, we help businesses:
- Develop scalable SaaS applications tailored to business operations
- Implement on-premise software with high security and customization
- Integrate hybrid solutions for flexibility and efficiency
- Ensure smooth migration from traditional software to SaaS platforms
Whether you need a custom-built cloud application or an optimized on-premise system, PT. KDN provides expert software development solutions to enhance business growth.
Conclusion
Choosing between SaaS and traditional software requires careful consideration of costs, security, scalability, and business operations.
- SaaS software is ideal for businesses seeking affordability, accessibility, and low maintenance.
- Traditional software is best for companies that prioritize security, customization, and full ownership.
- A hybrid approach offers a balance between cloud flexibility and on-premise security.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.